Gsc International Ligustrum Leaf; Showing Typical Mesophytic Dicot Leaf; Cross Section
A cross-section through a leaf Features of leaves and their functions The role of stomata The control gas exchange in the leaf. Each stoma can be open or closed, depending on how its guard.

Department of Botany
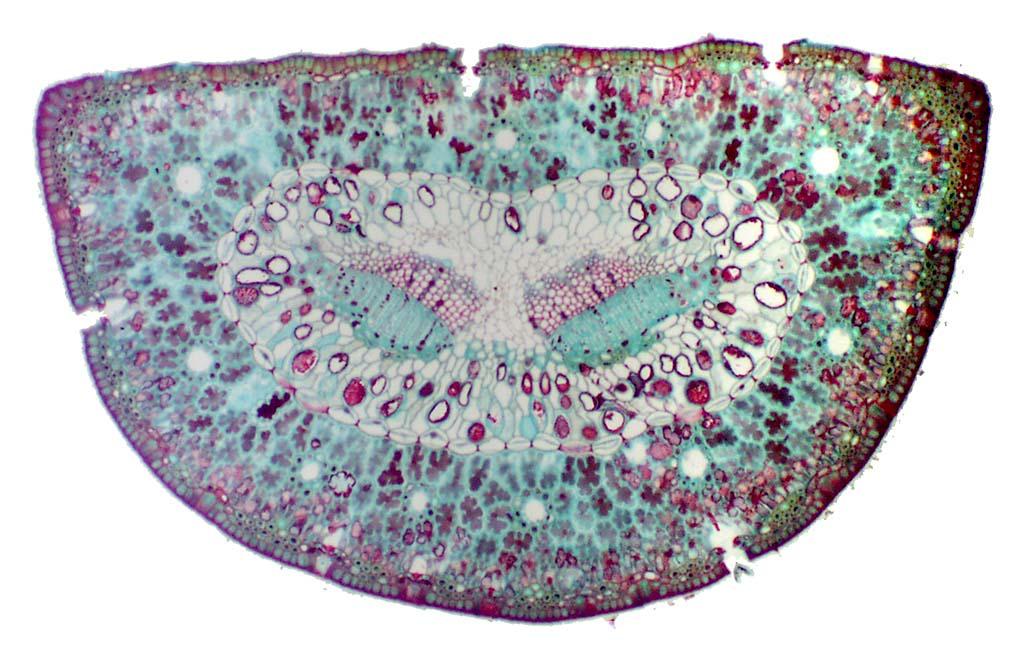
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): A cross section of a corn (Zea mays) leaf. See the caption in Fig. 13.2.3 for a detailed description of the features present. Photo by Maria Morrow, CC BY-NC. Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): A cross section of a section of a corn leaf, labeled. The upper epidermis is composed of parenchyma cells that appear empty.
Cross section of pine leaf UWDC UWMadison Libraries
Lab Objectives. At the conclusion of the lab, the student should be able to: List and give the major function of the three main types of plant tissues. Identify a monocot verses a eudicot plant by observing either root, stem, leaf, or flowers. Name and describe the various components and tissues within the root, both monocot and eudicot.

Cross Section Of Leaf Diagram Class 10 Ncert Class X Science / Cross section of a leaf. pradaden
Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\): Cross section of a pine leaf (needle). Much like the Nerium leaf, this leaf is coated in a thick cuticle and there is a hypodermis below the epidermis (because this leaf is so round, there is not really a distinct 'upper' and 'lower'). There are no stomatal crypts, but the stomata are sunken, located in the hypodermis.

Cross Section Of Leaf Stock Illustration Download Image Now iStock
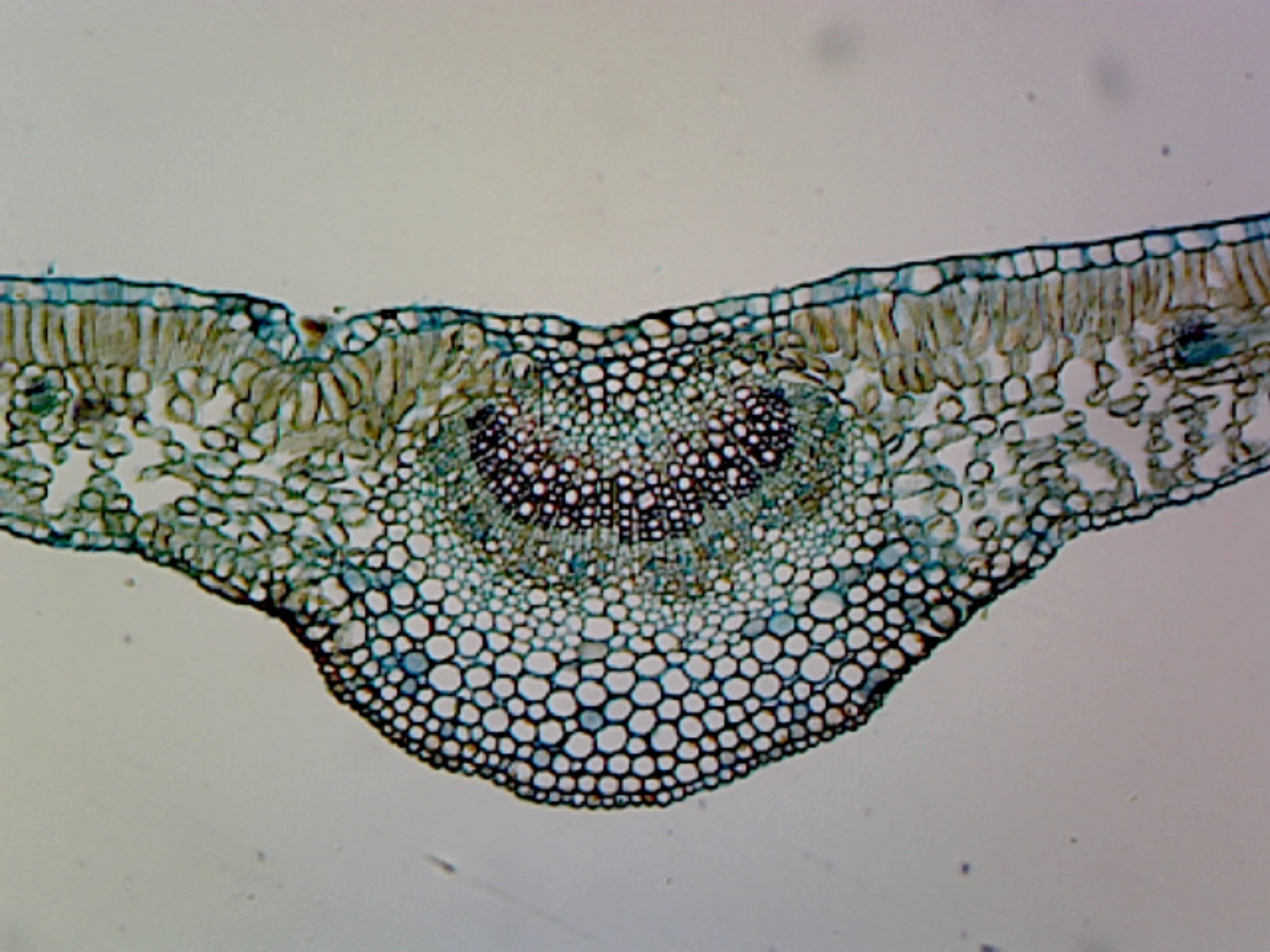
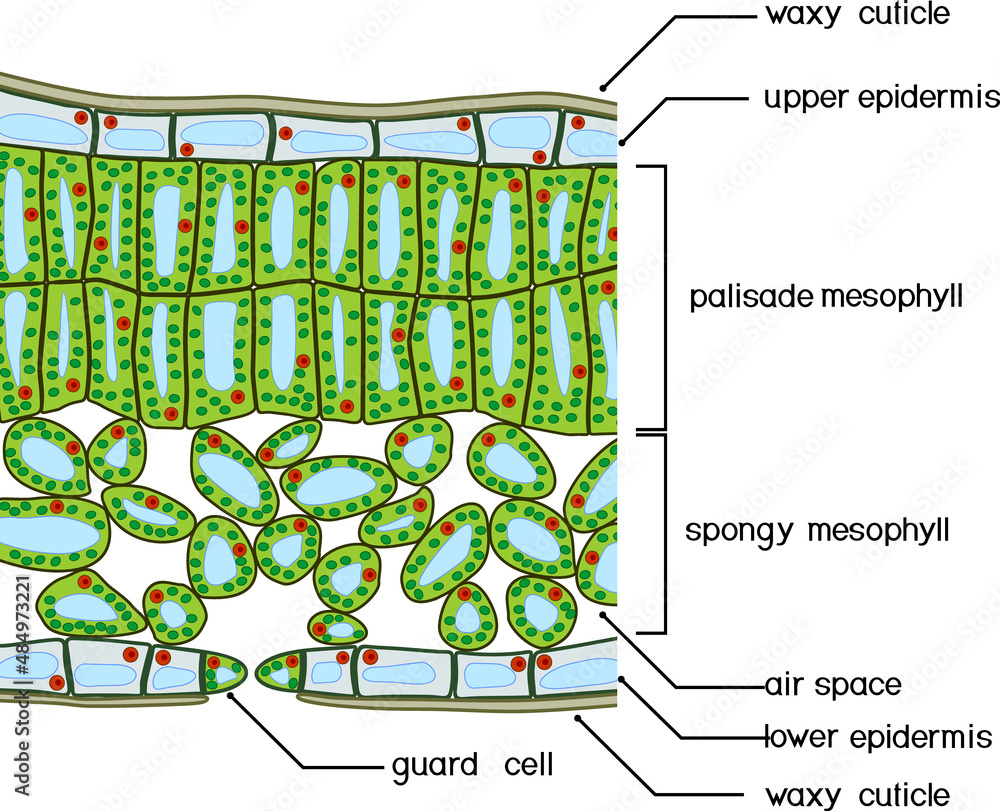
The structure of the umbrella tree leaf is typical of leaves in general (Above left photo). It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating. The epidermis of the undersurface produces guard cells, which swell and shrink to close and open the pores (stomata) which control the loss of water vapor (transpiration) and.

Cross Section Of Leaf Xylem And Phloem
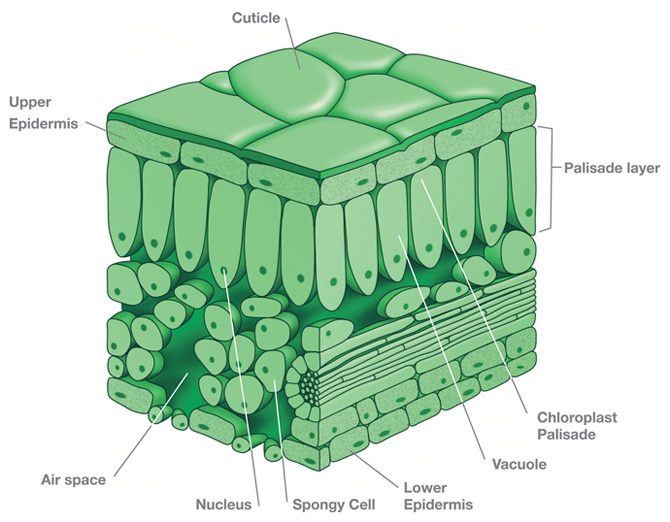
The air space found between the spongy parenchyma cells allows gaseous exchange between the leaf and the outside atmosphere through the stomata. In aquatic plants, the intercellular spaces in the spongy parenchyma help the leaf float. Both layers of the mesophyll contain many chloroplasts. Figure 30.10. 1: Mesophyll: (a) (top) The central.
Cross section of a leaf blade of Nerium oleander a xeromorphic plant UWDC UWMadison
Leaves are part of the shoot system of the vascular plant sporophyte and one of the three major vegetative (non-reproductive) organs types found in vascular plants (the others are stems and roots). The primary function of leaves is to carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which a plant makes its food.
Leaf Structure & Evolution Digital Atlas of Ancient Life
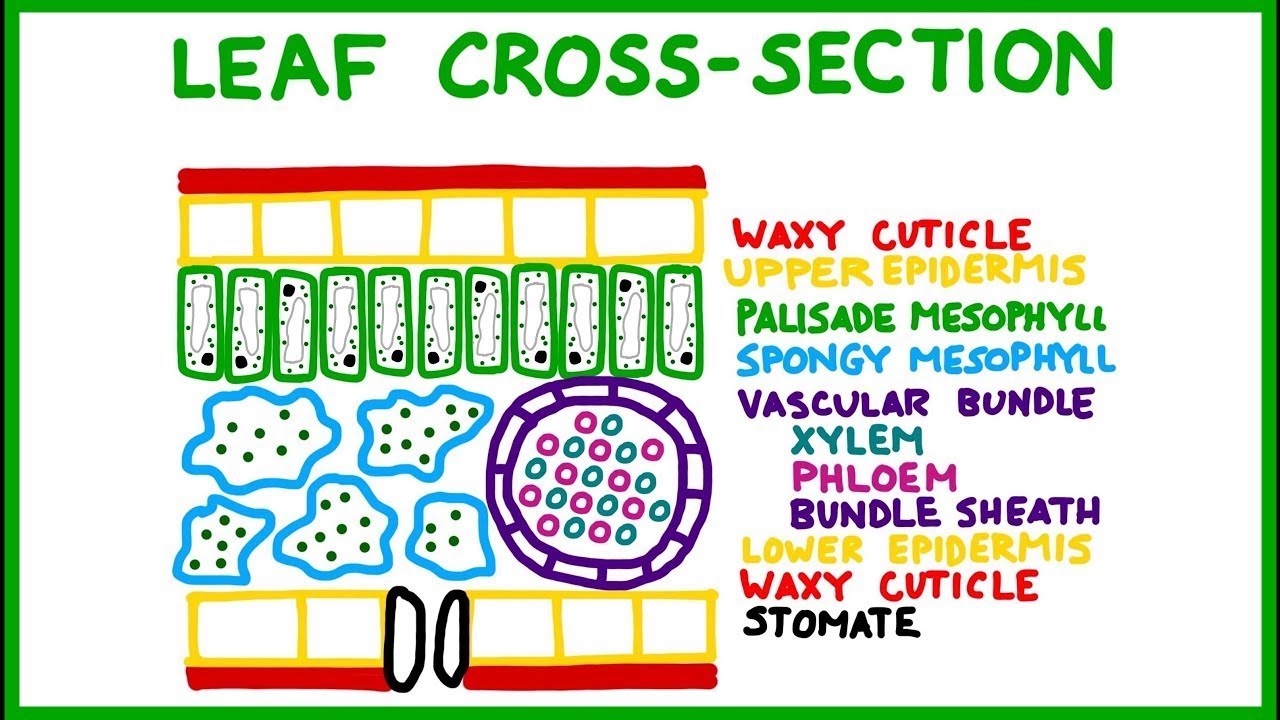
PHOTOSYNTHESIS [INTRO] Parts of a Leaf CrossSection of leaf.mov CROSS SECTION OF A LEAF Cuticle: A waxy layer that prevent water loss by evaporation. The cuticle is transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration. Upper Epidermis: A protective layer of cells that produces the cuticle.
Leaf CrossSection (Old version!) YouTube
Updated on November 04, 2019 Plant leaves help to sustain life on earth as they generate food for both plant and animal life. The leaf is the site of photosynthesis in plants. Photosynthesis is the process of absorbing energy from sunlight and using it to produce food in the form of sugars.

Cross Section of a Leaf Biology Diagram
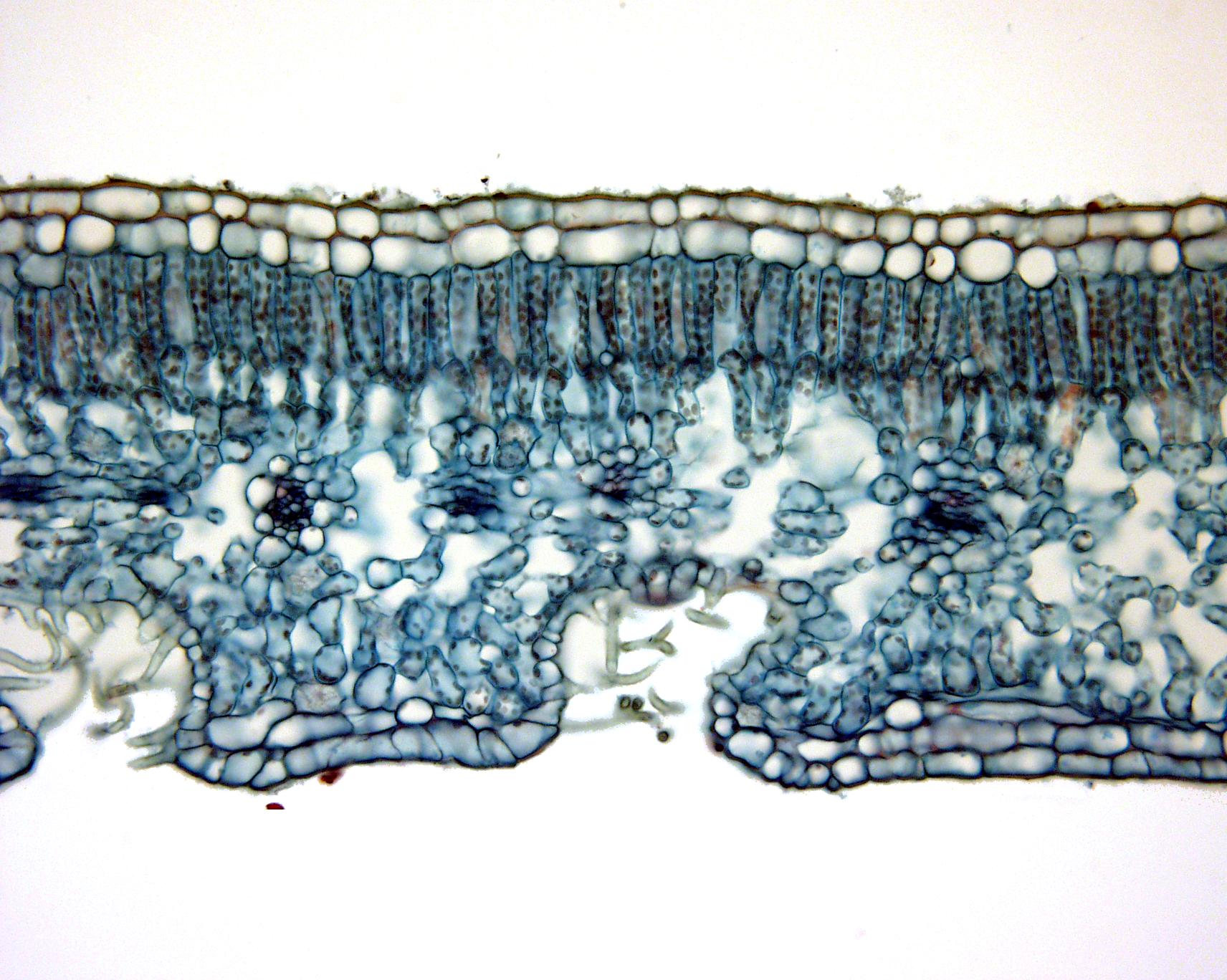
Cross-Section : In this view we see the upper and lower epidermis are one layer thick. While it is not obvious from these slides, a waxy cuticle is present on the leaf surfaces.The ground tissue is divided into two distinct regions: 1. the palisade parenchyma and 2. the spongy parenchyma. These are the primary photosynthetic tissues in lilac.
Plants Leaves
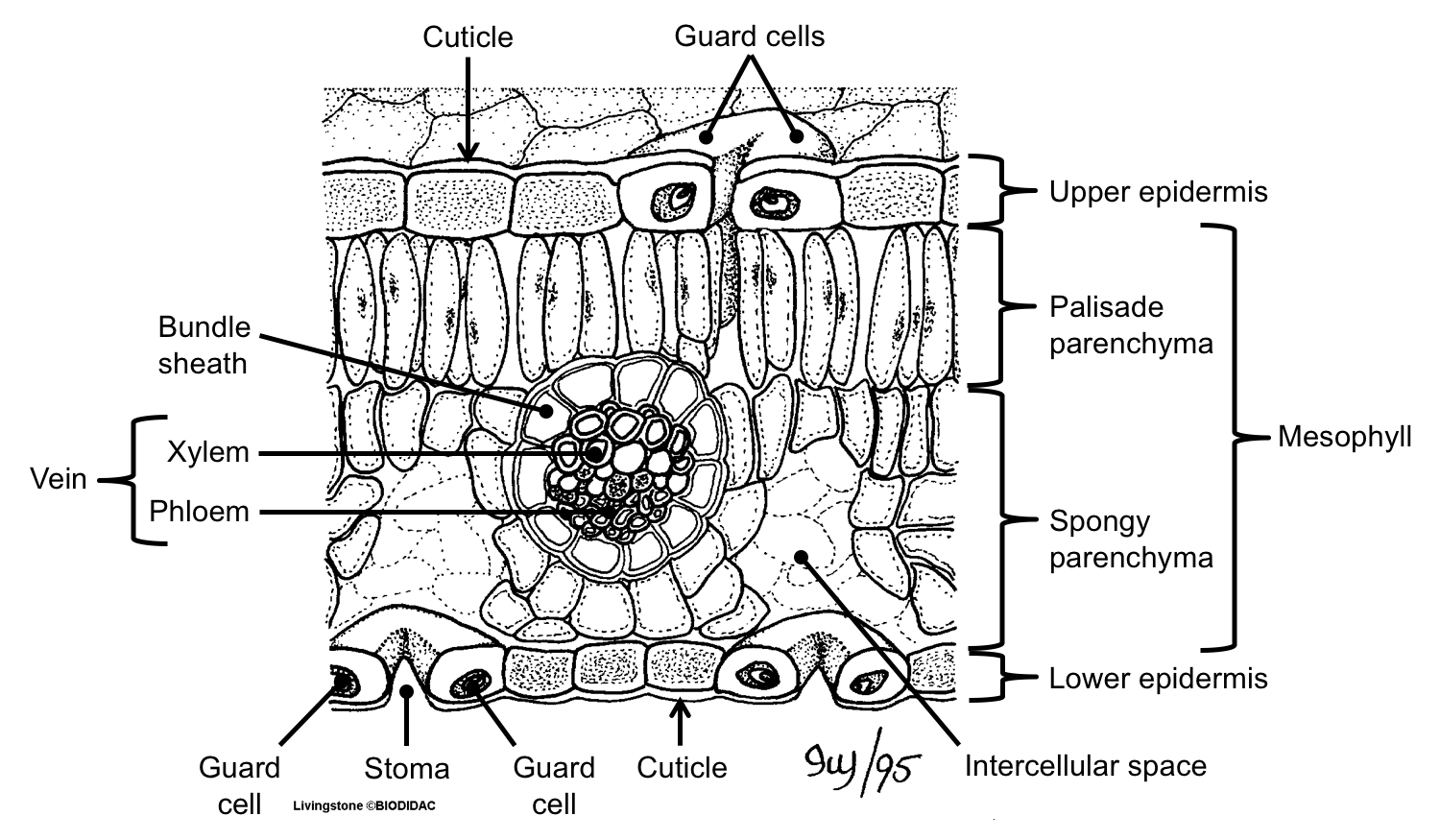
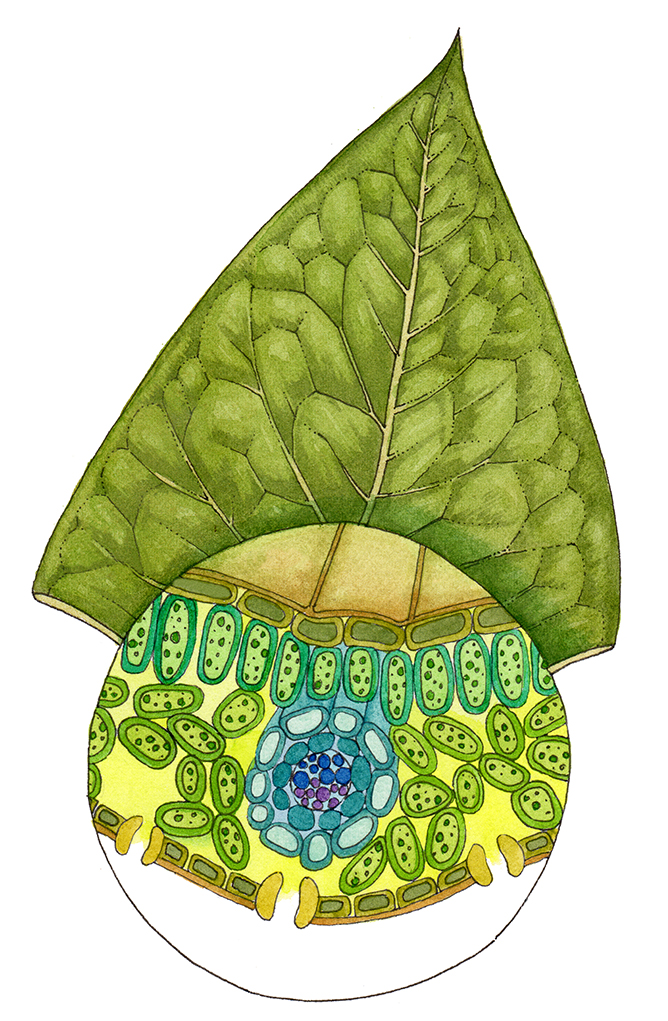
A cross-section through a leaf showing its main parts Light A leaf usually has a large surface area, so that it can absorb a lot of light. Its top surface is protected from water loss,.
Leaf cross section diagram Lizzie Harper
Plant Nutrition 6.5 Leaf Structure 6.5.1 Leaf Structure. 6.5.1 Leaf Structure. Download PDF. Structure of the Leaf . Diagram showing the cross-section of a leaf . How photosynthesising cells obtain carbon dioxide . Pathway of carbon dioxide from atmosphere to chloroplasts by diffusion:
Sectional diagram of plant leaf structure. Crosssection through a leaf Stock Vector Adobe Stock
Using a sharp razor-blade (I like the "Pal" single-edge carbon steel blades) make a single cut holding the blade against the edge of the upper slide, then a second cut with the blade angled in.

Cross Section Of A Leaf Diagram
You can see these if you look at a transverse section (cross-section) of a leaf under a microscope. 1. Cuticle: made of wax - waterproofing the leaf secreted by cells of the upper epidermis 2. Upper epidermis thin and transparent - allows light to pass through no chloroplasts are present act as a barrier to disease organisms 3. Palisade mesophyll
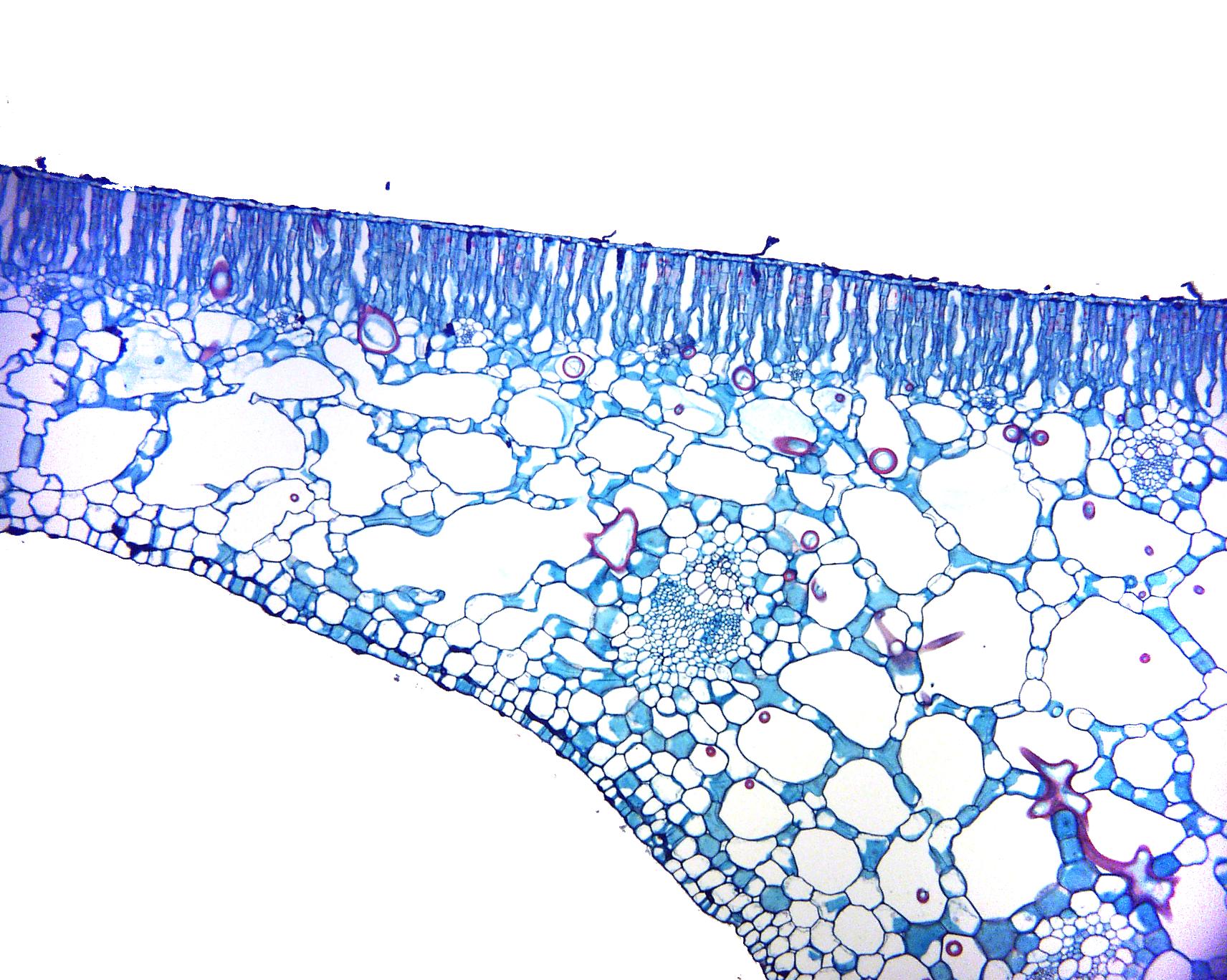
Cross section through a water lily leaf UWDC UWMadison Libraries
Solution Cross-section of leaf: Cuticle: The thin waxy layer that can control or prevent any loss of water from the leaf is called cuticle. Epidermis: The outermost later of the leaf which is present both on the upper and lower surface of the leaves is called epidermis.

Labeled cross section of a lilac leaf UWDC UWMadison Libraries
A cross section of a leaf shows that it is a complex organ built of several different kinds of specialized tissues. The tissues, in turn, are built of specialized cells, and the cells, of organelles. [Figure1] Epidermis covers the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf.